Best Practices
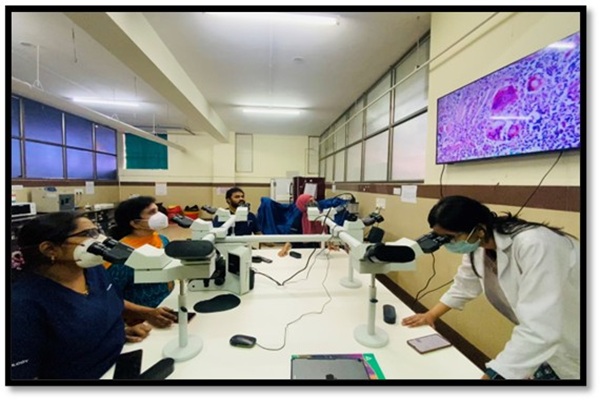
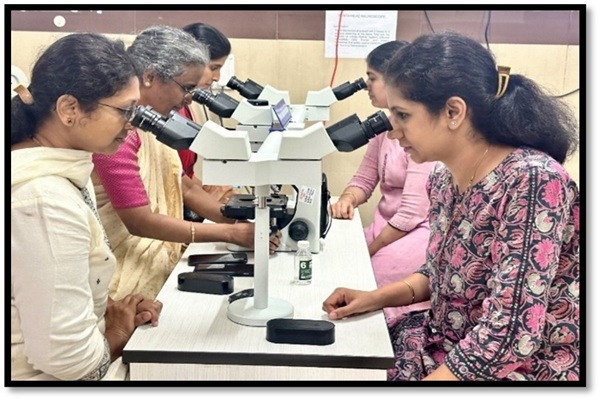
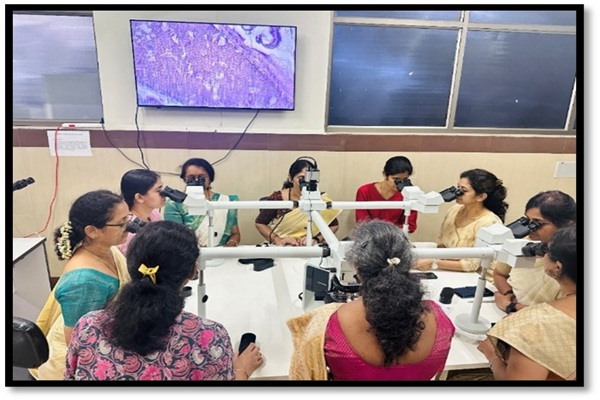
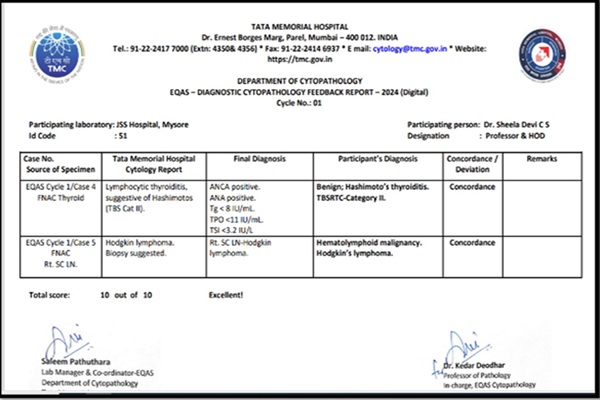
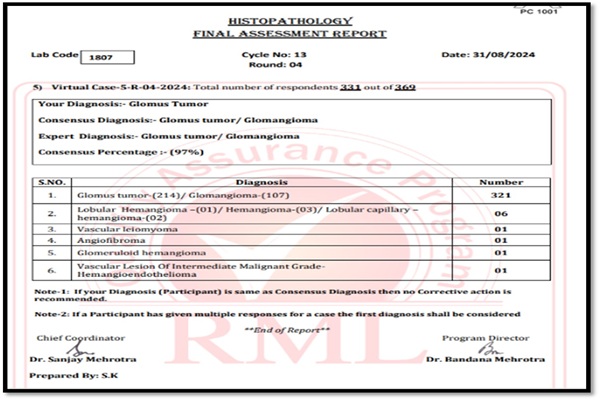
Unified vision for accurate diagnosis: multi head microscope/ whole slide imaging for consensus building in pathology
Context
Quality assurance with the aim of error reduction is an important component in pathology. Occasional difficult cases necessitate Intradepartmental consultation (IDC) when a consultant pathologist seeks a second opinion from another consultant pathologist within their department on a particular case prior to authorisation of the final report.
Intradepartmental consensus diagnosis utilizing a multi-headed microscope, or a projector is a highly effective form of solicited peer review that is best categorised as a quality improvement process measure that reduces pathology errors.
Objective
The consensus diagnosis practice is a useful method to
- Reduce intradepartmental diagnostic discrepancies and potential interpretive errors
- More detailed pathology report that potentially is more meaningful for the clinician with improved clarity of reports
- More effective patient care.
The Practice
The histopathologic diagnosis of interesting and challenging cases is made by presentation of the cases by the faculty at the multihead microscope. The cases are selected due to diagnostic difficulty, unusual nature, for management purposes such as performance of additional biopsies, special studies etc. or request on the part of clinician or patient.
The histological, ancillary and practical aspect of each case is discussed and a final consensus of opinion regarding diagnosis or management of each case is documented.
The pathologists take this opportunity to ask thought provoking questions, review the current standard of practice and the literature.
Obstacles
Differences in terms/nomenclature, threshold and philosophical/conceptual differences.
Strategy
Resolution of disagreements with re-review of the case with discussion among faculty. Disagreements addressed with review of additional slides to confirm or rule out features. In case consensus cannot be reached, the use of terminology that reflects the uncertainty of the diagnosis for appropriate resolution of the process, considering patient safety and appropriate management.
Impact of the practice
- Harmonization of nomenclature of the individual lesions
- Improved diagnostic accuracy
- Decrease in potential interpretive errors
- Reduction in intradepartmental diagnostic discrepancies
- Enhanced completeness and timeliness of all surgical pathology reports
- Can close knowledge gaps and decrease the use of imprecise terminology.
Resources Required
Decahead/ Penta head Microscope, Whole slide imaging
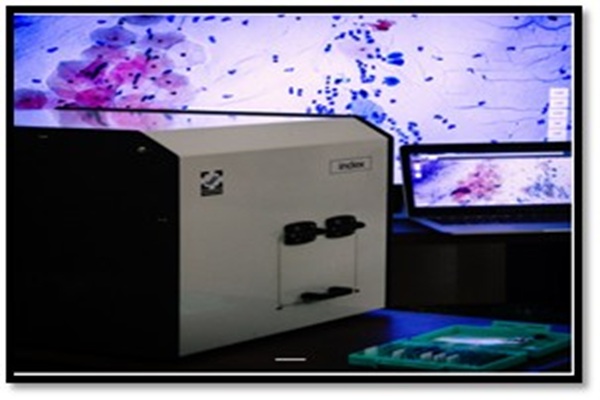




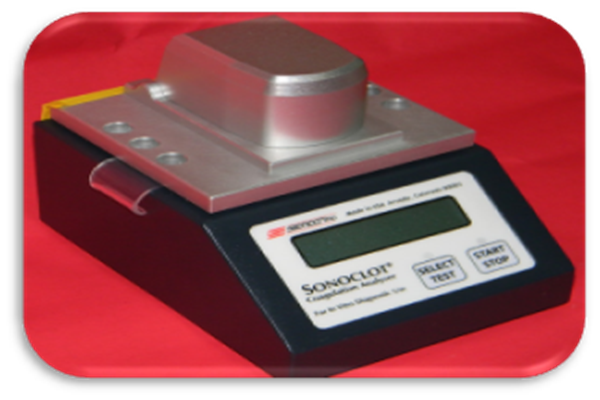
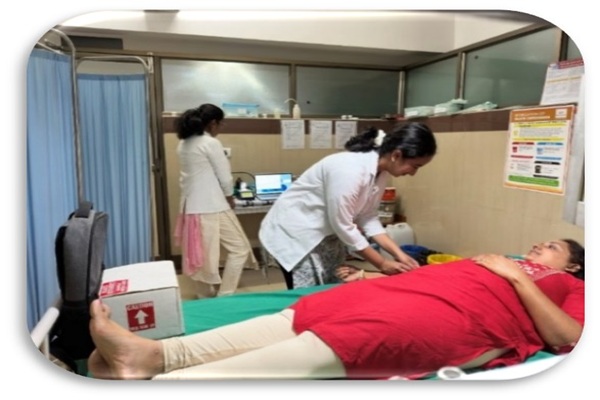
SONOCLOT: Cost effective portable device for haemostasis assessment anytime, anywhere
Context
SONOCLOT is a point of care device working on the principle of viscoelastometry for the assessment of complete hemostasis right from the point of initial fibrin thread formation to the rate of clot formation and strength of the clot formed. Thus all aspects of hemostasis, namely coagulation factors, fibrinogen activity and platelet function will be assessed at once. It is a boon especially for the hemostatic management of critically ill patients in ICUs, patients with DIC, commonly encountered complication in ICU cases, post operative bleeding cases, bleeding patients in emergency department are the chief beneficiaries of this point of care device. It can be effectively utilized as a screening tool for assessment of platelet function.
Objective
- To assess the complete hemostatic status of the critically ill patients in the ICUs who are in need of hemostatic support
- For effective management of patients with DIC
- For pre-operative screening of hemostatic status before major surgeries
- To evaluate a bleeding patient in emergency department.
- To screen for platelet functions.
The Practice
Sonoclot being a point of care device is taken near the patient. The device is connected to the computer and software is opened. The device temperature will start rising till it attains 370C. Once the device temperature is 370C, cuvette is placed in the cuvette holder of the device and probe in its position. After 5 minutes, blood is drawn, and 350 micro litres of blood is put into the cuvette and start button is pressed on the device. Blood sample will start getting mixed with the glass bead activator within the cuvette. After mixing is completed, the head of the device is closed as per the instruction given by the device. Then, graph will be plotted on the computer monitor and three parameters of the Sonoclot, ACT, Clot Rate (CR) and Platelet Function (PF) values will be displayed.
Obstacles
Experience and meticulous conduct of the procedure being the requirement, failing to follow the SOP strictly can result in erroneous graph pattern and test result.
Strategy
Regular quality check by the inbuilt QC module within the device and supervised training of the personnel in conducting the test.
Impact of the practice
- Judicious and appropriate usage of blood products in critically ill patients and patients with DIC in ICUs
- Effective preoperative screening of hemostatic status in patients undergoing major surgeries.
- Effective evaluation of postoperative bleeding
- Effective evaluation of bleeding patient in EMDs
- Effective screening of patients for platelet function at a reasonable cost.
Resources Required
SONOCLOT (device), Cuvette and the probe (consumable), Computer system with software installed.

Blood shield: hemovigilance for ensuring the safe blood transfusion
Context
Haemovigilance is a set of surveillance procedures covering the whole transfusion chain, from the collection of blood and its components to the follow-up of its recipients, intended to collect and assess information on unexpected or undesirable effects, resulting from the therapeutic use of labile blood products and to prevent their occurrence and recurrence.
Objective
- Monitor Transfusion Reactions
- Create awareness amongst healthcare professionals about safe blood transfusion practices
- Evidence based recommendations
- Advise CDSCO for safety related regulatory decisions
- Communicate findings to all key stakeholders
The Practice
- Blood unit/units are issued after entering details of blood bag in issue register and taking signature from residents / interns/ nursing staff
- Transfusion reaction form and the consent form is issued along with every unit.
- The end users are educated to take the consent before transfusion.
- They are also informed to monitor every transfusion and fill up the Transfusion reaction form irrespective of the adverse reaction and return the form along with the empty blood bag.
- In case of adverse transfusion reaction - Transfusion Reaction Work-Up is done in the department and the reaction is characterized accordingly. The details are entered in the reaction workup form and the same is submitted to the Haemovigilance Programme of India (HvPI), National institute of biologicals through online portal.
Obstacles
Prompt identification and reporting of adverse transfusion reaction at the user end by nursing staff, interns and residents at wards, intensive care units and operation theatres is needed.
Strategy
Strategies to overcome them: Blood transfusion policies were formulated through Hospital Transfusion Committee incorporating transfusion consent forms and transfusion reaction forms for all transfusions. Interns and residents were oriented about the best practice procedure. Teaching sessions with awareness and knowledge about best practice by Transfusion Medicine consultants were made part of regular teaching activity for the nursing staff.
Impact of the practice
Awareness about Adverse Transfusion Reaction among the health care professionals leading to safe blood transfusions.
Resources Required
- Printing of transfusion reaction form/transfusion evaluation form.
- Computer and internet connection for online reporting of adverse transfusion reaction to NIB under Hemovigilance program of India.
| Year | Total number of units issued | Total No of Adverse Transfusion Reaction | ATR % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 18152 | 31 | 0.17 |
| 2019 | 18195 | 27 | 0.15 |
| 2020 | 15134 | 33 | 0.21 |
| 2021 | 14603 | 31 | 0.21 |
| 2022 | 15981 | 47 | 0.29 |
| 2023 | 13982 | 43 | 0.31 |



Project activity in each block
Context
Increasingly, medical educators are incorporating reflective writing and original creative work into educational practices with the goals of stimulating student self-awareness, and mastery through the application of their knowledge rather than rote memorization. The teacher's role becomes that of a guide and the students take ownership of their learning.
Objective
To involve students in higher-order thinking tasks as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
The Practice
Students are assigned cases covering many organ systems and diagnoses with brief clinical vignettes pointing to the diagnosis, and an additional study or clinical test. With this they make the final diagnosis and discuss the pathology of the disease using innovative strategies such as making presentations, concept maps, e-posters, skits, blackboard teaching, presentations, mime, role play and jingles. Criteria for assessment included content, conceptualisation and presentation.
Obstacles & Strategy
Equal participation of all students. Each student is required to actively demonstrate participation.
Impact of the practice
Developing communication skills among students.
Resources Required
Galleries, classrooms, with projectors and stage.


Conversion of dissertations to manuscripts
Context
Publishing one’s academic work as articles in peer-reviewed journals, are a tangible touchstone of scholarly achievement. It is an opportunity to present the work to a wider audience, which harbours opportunities for further research leading to career growth of the researcher and recognition by a professional body which surpasses the institution's internal corridors.
Objective
To publish more than one article from the dissertation without overlapping any of the content across the articles in a journal that is peer-reviewed has a high academic rigor, ranking, and reputation and is indexed in databases that are credible and recognized in the field.
The Practice
Following completion of the dissertation, the steps for conversion to suitable manuscripts include collaboration with guide and co-guide, journal identification, manuscript reformat including creating a coherent story/argument, targeting the journal readership and changing the writing conventions from that used in the thesis.
Obstacles
Reducing redundant length of the dissertation without affecting the essence and context of the research. Cost for submission, editing, and formatting.
Strategy
Using a multiple-paper format when initially writing the dissertation or thesis by structuring the dissertation or thesis used to fulfil the requirements as a series of shorter papers that are already formatted for journal submission and including only the most pertinent references.
- Applying for grants from University and ICMR when reasonable and requested by reputable publishing houses.
Impact of the practice
- Enables graduates to begin publishing career, advance their academic career and establish valuable connections that can open doors for collaborating on future projects.
- Increase in Scholarly output, Cited publications of the institution
- Dissemination of research findings
- Successful publication of research brings attention to scholars and their institutions which may bring in more funding for the institute and also ensure an individual's progress through their field.
- Increased measure of competency in researcher’s profile
Resources Required
Access to clinical data, archived slides and blocks, writing and referencing tools, workshops on selection of journals.

