Welcome to Institutional Biosafety Committee
In accordance with the Rules for the use and storage of hazardous microorganisms/ genetically engineered organism/plants/cells, Government of India, Under the Environment Protection Act, 1986, has enforced rules and regulations on the biosafety and biocontainment of hazardous, recombinant DNA, synthetic nucleic acids and use of hazardous biomaterials of any kind. Under the guidelines of this act, JSS Academy of Higher Education & Research, Mysuru, has constituted - Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) as per DBT, Government of India guidelines.
Our Mission
The primary mission of the IBSC is to ensure the safety of faculty, and the researchers involved in the biological research at our institute and to protect the general public and the environment from adverse consequences of the proposed research.
Purpose of IBSC
The IBSC is responsible for reviewing projects that involve, but are not limited to, recombinant DNA, RNAi, pathogens, human materials (specimen's repositories) and other potentially infectious material, as well as transgenic animals, genetically modified plants and seeds, CRISPER and Gene knockouts, bacterial and viral vectors based transfections. The IBSC provides recommendations in matters pertaining to the control of biohazards associated with the use of microbiological agents and their vectors and related research.
The IBSC will determine approval or recommendations of the proposed experiments through review of the application submitted by the principal investigator along with supporting materials. This review and oversight involves independent assessment of the biosafety containment level proposed for the work and through coordination with the biological safety officer, assessment of facilities, procedures, practices, training and expertise of personnel involved in the research.
Specifically, the IBSC will review research proposals with the following potentially hazardous biological agents and experiments
- Recombinant DNA and synthetic nucleic acid molecules
- Infectious agents
- Biological toxins
- Certain animal-derived tissues, fluids, and cells
- Transgenic animals/plants
Composition of the IBSC Committee
| IBSC Members | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Basavangowdappa H, Chairman, IBSC, JSS AHER | hbgowda@gmail.com |

|
| Dr. Sumana M N, Biosafety Officer, IBSC, JSS AHER | mnsumana@jssuni.edu.in |

|
| Dr. Asha Srinivasan, Member Secretary, IBSC, JSS AHER | Asha.srinivasan@jssuni.edu.in |

|
| IBSC Internal Members and Research Staff | ||
| Prof. SubbaRao MVSST, Internal Member, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Saravanababu C, Internal Member, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Ashish D Wadhwani, Internal Member, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Mohan T C Internal Member, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Divya P Kumar, IBSC Research Staff, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Akila Prashanth, IBSC Research Staff, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Devananda Devegowda, IBSC Research Staff, JSS AHER |

|
|
| Dr. Muthukumar S P, External Member, CFTRI, Mysuru |

|
|
| Dr. Ramachandra Kini, External Member, University of Mysore, Mysuru |

|
|
| Dr. Ravindra P V, External Member, CFTRI, Mysuru |

|
|
| DBT Nominees | ||
| Dr. Manjuntha H B DBT Nominee, University of Mysore, Mysuru |

|
|
| Dr. Shylaja R DBT Nominee, DFRL, Mysuru |

|
|
| Dr. Nandini C D DBT Nominee, CFTRI, Mysuru |

|
|
Role of IBSC
The IBSC has to meet at least twice a year to review the status of projects involving biohazardous, human materials, recombinant DNA. It is important that the Chairman and Member Secretary ensure that regular meetings take place. More than two meetings may be held as per requirement of the projects. The IBSC members are expected to look into the following during the meetings
- Action taken on the decisions of the earlier IBSC meetings.
- Characterization of work and approval as per risk category.
- Evaluation of projects and direction to submission for appropriate agencies for approvals.
- Maintaining procedures and other approval requirements.
The role of IBSC assumes major importance in the regulatory framework since it is a Statutory Committee that operates from the premises of the institution and hence is in a position to conduct onsite evaluation, assessment and monitoring of adherence to the biosafety guidelines. The functions in the IBSC of the head of the organization, members, DBT nominees, Principal Investigator and Member Secretary are explained below
Chairman of IBSC
- The chairman of IBSC has the responsibility to ensure that the biosafety guidelines are followed in his/her institution.
- Regular meetings of IBSC are held to review rDNA research and infectious agents-involving projects in the institution.
- Open discussion takes place amongst the members in the meetings and the views of external members as well DBT nominee are recorded.
- The facilities at the institution are sufficient to meet the containment levels stipulated for rDNA research and processes.
The chairman of IBSC has the responsibility to ensure the biosafety guidelines are followed in accordance with the DBT regulations for the use and disposal of biohazardous materials. Conduct regular meetings with the internal/ external, and DBT nominated members. It is important that the Chairman and Member Secretary ensure that regular meetings take place. More than two meetings may be held as per requirement of the projects.
Biosafety Officer
Advise on risk assessment for all proposed work with biological agents. Advise on biohazard waste disposal arrangements. The biosafety officer must ensure that the facilities at the institution are sufficient to meet the containment levels stipulated for biohazardous work and disposal.
DBT Nominee
The IBSC has a nominee from DBT who oversees the activities to ensure that safety aspects are being fully adhered to by the organization. The DBT nominee serves as the link between the department and the respective IBSC. In addition to the responsibilities as an IBSC member, the duty of the DBT nominee is to ensure that
- The committee has been constituted as per the norms of the guidelines.
- The recombinant DNA Safety Guidelines are strictly followed in the institution.
- The IBSC meets regularly, at least twice in a year to review the ongoing activities and provides half yearly reports to RCGM/DBT in the prescribed proforma.
- All the activities are within the preview of the guidelines and in the knowledge of RCGM/DBT.
- The DBT nominee is expected to guide the IBSC on biosafety issues.
Member Secretary
Works in accordance with the Chairman, Biosafety officer and DBT nominees for smooth conduct of IBSC activities. Schedules meetings, IBSC training and coordinate all activities of IBSC. Meetings will be conducted once in 6 months or on the basis of received proposals. Member secretary will be responsible for getting confidentiality agreement signed from the external members and DBT nominees.
Project Principal Investigators
All recombinant research projects carried out by an organization have a Principal Investigator (PI) and it is the duty of the PI to apprise the IBSC about the nature of the experiments being carried out. Depending upon the risk category, the PI has to inform the IBSC, seek permission of IBSC before starting the experiments or seek permission of the RCGM through its IBSC.
The PI is primarily responsible for ensuring compliance with biosafety standards. The PI functions as a project manager as well as a researcher, communicating with the IBSC and bearing responsibility for training and supervising personnel.
Based on the nature of the GMO or the infectious agent, the PI determines the proper containment level for the project and, in accordance with the DBT Guidelines, develops the necessary experimental protocols. This information is then submitted to IBSC for review.
The responsibilities of PI to IBSC are summarized below:
- To make an initial determination of the required levels of physical and biological containment in accordance with the DBT guidelines.
- To submit the initial research protocol and any subsequent changes (such as changes in the source of DNA or host vector system) to the IBSC for review and approval.
- To ensure that no work is initiated until the research project has been approved by the IBSC and has met all requirements of DBT guidelines.
- Remain in communication with the IBSC throughout the conduct of the project.
- To ensure the safe conduct of the rDNA experiments in his/her laboratory.
- To make available the protocols that describe the potential biohazards and the precautions to be taken to all laboratory staff.
- To nstruct laboratory staff about the practices and techniques required to ensure safety, and the procedures for dealing with accidents including the reasons and provisions for any precautionary medical practices advised or requested (e.g. vaccinations or serum collection).
- To supervise the performance of the laboratory staff to ensure that the required safety practices and techniques are employed.
- To undertake corrective measures promptly for any work errors and conditions that may result in the release of recombinant DNA materials or the infectious agent.
Laboratory Personnel (Technician, Technologist, Student, Post-doctorate, Young Investigators)
THE Laboratory personnel must
Follow all safety guidelines and establish good laboratory practices. They must work within the assigned biological safety containment level and use personal protective equipment as recommended.
- Immediately notify the PI or Biological Safety Officer (BSO) of any health condition that may be due to their work in the laboratory or any health condition that may be compromised prior to the initiation of a research project (i.e. pregnancy, immunosuppression).
- Follow all practices and procedures as provided by the PI and BSO, and ensure strict compliance with all required biosafety regulations and guidelines.
- Report problems, procedural mistakes, spills, etc. to the PI, and if necessary to the BSO, immediately.
- Report to the PI, BSO or IBSC on non-compliance of biosafety guidelines or policies.
IBSC Guidelines
The purpose of these guidelines is to provide guidance to organisations that have Institutional Biosafety Committees (IBSCs) or intend to set up an IBSC in compliance with “Rules for the manufacture, use/import/export and storage of hazardous microorganisms/ genetically engineered organisms or cells, 1989” (hereinafter referred as Rules, 1989) notified by the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF), Government of India under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Guidelines for submitting application for ethical clearance by the IBSC
The current scope of the IBSC covers research involving
- Recombinant DNA molecules or synthetic nucleic acids including transgenic animals or plants.
-
Biological agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, parasites, and prions) and/or vectors that carry biological agents (arthropods, snails, etc.) which:
- cause or are reasonably expected to cause disease in immunocompetent humans; or
- cause or are reasonably expected to cause significant disease in local livestock (including poultry), agricultural crops, or indigenous wildlife
- Acute biological toxins having an LD50 < 100 ng/kg in mammals
- Human or nonhuman primate blood, blood products, tissues, secretions, excretions, or cell lines unless documented to be free of bloodborne pathogens or are otherwise low risk as per written risk assessment.
- Venomous animals posing a risk to humans through bite or sting and housed and/or manipulated in laboratories or other indoor facilities
- Poisonous plants posing a risk to humans via dermatological contact, inhalation, or other route of exposure and housed and/or manipulated in laboratories or other indoor facilities
- Novel nanoparticles conjugated to biologically active or cell-modifying molecules
Submit a hard copy of the application to the office of the Member Secretary, IBSC. A soft copy of the application should also be submitted via email: ibsc@jssuni.edu.in
The application form can be downloaded from the following links:
IBSC Meeting Schedules
Please note that the IBSC normally meets every SIX months (November and May), therefore the application should be submitted at least 30 days in advance (i.e., by September 30 for the November meeting, and by March 31 for the May meeting).
It is the duty of the primary investigator (PI) to apprise the IBSC about experiments involving biohazardous materials, use of recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology, genetically modified organisms (GMOs) or living modified organisms (LMOs) through the application as stated above. This should be done prior to submission of a grant application to a funding agency.
While preparing the application please note the following:
- For experiments involving rDNA, The PI must determine the biosafety level as well as the category that the experiments fall under based on the guidelines provided on page 187 in the following document
Recombinant DNA Safety Guidelines of DBT - The assignment of the risk category of any microorganism(s) being handled as part of the experimental protocol must be determined based on the information provided in the pages 208-220 of the following document
Recombinant DNA Safety Guidelines of DBT
Please go through the guidelines provided by DBT in the following document to understand the responsibilities of the PI
IBSC Guidelines Handbook - 2020
STEP 1: The application will be evaluated by the committee (and subject expert if required) and the applicant may be asked to provide other documents if required.
STEP 2: A meeting of IBSC will be scheduled and the date will be communicating to the applicant at least 20 days in advance. The applicant may be asked to present his/her proposal to the committee and a decision will be communicated to applicant within a week
All applicants are advised to go through the Indian Biosafety Rules & Regulations
Code of practice in Laboratory
- Biohazard symbol should be placed at the entrance of recombinant DNA work area
- Access to the laboratory should be limited or restricted only to the workers
- Eating, drinking, smoking, storing food, and applying cosmetics should not be permitted in the laboratory work area.
- Laboratory coats, gown or uniforms should be worn while in the laboratory. The protective clothing should be removed before leaving laboratory for non-laboratory areas.
- Gloves should be worn while handling the rDNA materials and infectious agents to avoid skin contamination
- All contaminated liquid or wastes should be decontaminated by ethanol treatment or autoclaving before disposal
- Contaminated materials should be stored in leak-proof containers till decontamination
- Mechanical pipetting devices should be used; mouth pipetting is prohibited.
- Work surfaces are decontaminated at least once a day
- Persons should wash their hands after handling recombinant DNA materials and infectious agents.
- Creation of aerosols should be minimized.
- Biological Safety Cabinets should be used for routine work with rDNA materials and infectious agents.
- Control measures should be taken to avoid entry of insects and rodents.
- Spills and accidents which result in rDNA exposures, or exposure to infectious organisms should be immediately reported to laboratory in-charge and IBSC.
Code of Practice for Containment Laboratory
The code of practice for a basic laboratory applies as follows except where modified
- The two-person rule should apply, whereby no individual works alone within the laboratory.
- A hazard warning sign should be displayed on laboratory doors, identifying the agent, the name of the laboratory supervisor and other responsible person(s) and indicating any special conditions of entry into the area (immunizations, etc.).
- Laboratory clothing that protects street clothing (i.e. solid front or wrap-around gowns, scrub suits, coveralls, etc.) must be worn in the laboratory. Laboratory clothing must not be worn outside the laboratory and must be decontaminated before being laundered.
- When appropriate, respiratory protective equipment should be worn in rooms containing infected animals.
Handling Bio-hazardous Materials
- Skin exposure: Vigorously wash affected skin with plenty of soap and water while removing contaminated clothing and shoes.
- Eye exposure: Wash eyes for at least 10 minutes with plenty amounts of water, lifting the upper and lower eyelids occasionally.
- Seek follow-up medical attention by contacting your supervisor for referral to the medical facilities or for medical assistance call IBSC.
Procedure for Cleanup of Biological fluid/bacterial Spill and Reporting
Follow these procedures for cleaning-up spills of blood and blood products. The same procedures can be used for cleaning up other body fluids. For any assistance call IBSC. Prior to beginning the clean-up, wear personal protecting equipment (PPE) i.e. rubber, latex, PVC or similar type gloves, lab coat etc.
- The following items may be needed in handling the spill
- 10% bleach solution or Lysol
- Gloves
- Clear plastic bags
- Biohazard labels (available from IBSC)
- Leak-proof sharps containers
- Brush & dustpan, or tongs or forceps for picking up sharps materia
- Disinfectant wipes
- Gauze piece
- Cover all the spill area with a paper towel/blotting sheet and then pour freshly prepared mixed 10% bleach and water solution. Allow solution to soak into the contaminated material for 20-30 minute.
- Any glass, needles, or other sharp objects that may puncture the skin will should not be picked up by hand. Only brush and dustpan, or forceps are allowed to pick the sharp material.
- If you do not have such equipment available, contact IBSC for assistance. Wipe up bleached material with paper towels or absorbent pads. It may be necessary to use a scrub brush to remove the material and clean the area.
- If you do not have such equipment available, contact IBSC for assistance. Wipe up bleached material with paper towels or absorbent pads. It may be necessary to use a scrub brush to remove the material and clean the area.
- Place bleached material, gloves and other disposable materials into a labeled biohazard bag and place into either another labeled biohazard bag or container. Ensure lids are firmly sealed on all waste containers when spill clean-up is complete and keep biohazard waste container in a biohazard waste room until picked by biohazard waste agency.
Procedure for using hazardous chemicals

- Familiarize yourself with the potential hazards of chemicals. Keep record of MSDSs of the hazardous chemicals used in the laboratory.
- Evaluate the type of toxicity of the hazardous chemical (i.e. corrosive, irritant, sensitizer, and carcinogen), the possible routes of exposure (i.e. inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, injection) and hazards of flammable and explosive chemicals.
- Appropriate eye protection and protective apparel should be used during the chemical handling and follow the appropriate procedure to minimize exposure.
- Smallest container or the amount of hazardous material that will be used within a reasonable period should be purchased.
- First aid is always the top priority. If you spill a hazardous material on yourself, remove any potentially contaminated clothing immediately. Seek appropriate medical treatment.
- If material spills in your eye, flush for at least 15 minutes (for corrosive materials, you may need to flush for up to 60 minutes – review the (MSDS). Seek appropriate medical treatment.
- Use leak-proof containers, metal cans, or plastic-coated bottles for storing and transporting hazardous material.
- Do not place glass containers of chemicals on the floor and avoid fallen or leaking gas cylinders
Procedure for Cleanup of hazardous Chemical Spill and Reporting
- All staff and students in the biological laboratory/Chemical Laboratory who handle hazardous chemicals should be familiar with spill response procedures.
- The possibility of a spill and preparation for handling it should be anticipated in setting up your experiment. Appropriate precautions will alleviate many associated complications
- Ensure there are no ignition sources in the area. If you feel there is risk of fire or explosion, evacuate the lab and treat as a major spill.
- Alert people in the lab that a spill has occurred and ask them to evacuate; close doors to the affected area.
- If spilled material is flammable, turn off ignition and heat sources if it can be done safely.
- If it can be done safely, block off any drains where the spill may enter. Acids typically have a sour taste and a pH less than 7. Neutralize spill with Sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate/baking soda and wait until bubbling/fizzing has stopped.
- Bases have a bitter or a stringent taste and a pH greater than 7. Bases are also called alkaline compounds and are neutralized by using a weak acid. Common bases are sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide and ammonia. Neutralize spill with citric acid, sodium bisulfate.
- All spill residue and spill clean-up material need to be placed in a high-density polyethylene or polypropylene bag with attached hazardous waste tag.
Waste Disposal
As per Section 6, 8 and 25 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 of the Central Government the waste must be disposed-off in the following manner
| Cat. No. | Type of Waste | Examples | Treatment & Disposal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Human anatomical waste | human tissues, organs, body parts | Incineration@/deep burial* |
| 2 | Animal waste | animal tissues, organs, body parts, carcasses, bleeding parts, fluid, blood and experimental animals used in research, waste generated by veterinary hospitals colleges, discharge mfrom hospitals, animal houses | Incineration@/deep burial* |
| 3 | Microbiology & Biotechnology waste | wastes from laboratory cultures, stocks or specimens of micro-organisms, live or attenuated vaccines, human and animal cell culture used in research and infectious agents from research laboratories, wastes from production of biologicals, toxins, dishes and devices used for transfer of cultures | local autoclaving/micro-waving/incineration@ |
| 4 | Sharps contaminated with biological waste | needles, syringes, scalpels, blades, glass, etc. that may cause puncture and cuts. This includes both used and unused sharps | disinfection (chemical treatment@ /autoclaving /micro- waving and mutilation/shredding## |
| 5 | Discarded medicine & cytotoxic drugs | wastes comprising of outdated, contaminated and discarded medicines | incineration@/ destruction and drugs disposal in secured landfills |
| 6 | Solid waste contaminated with biological sample | Items contaminated with blood, and body fluids including cotton, dressings, soiled plaster casts, lines, beddings, other material contaminated with blood | Incineration@ / autoclaving / microwaving |
| 7 | Solid waste | wastes generated from disposable items other than the waste sharps such as tubings, catheters, intravenous sets etc. | treatment@@ /autoclaving / microwaving and mutilation/shredding## |
| 8 | Liquid waste | waste generated from laboratory and washing, cleaning, house-keeping and disinfecting activities | disinfection by chemical treatment@@ and discharge into drains |
| 9 | Incineration ash | ash from incineration of any bio-medical waste | disposal in municipal landfill |
| 10 | Chemical waste | chemicals used in production of biologicals, chemicals used in chemical disinfection, as insecticides, etc. | chemical treatment@@ and discharge into drains for fluids and secured landfill for solids |
Note
Chemicals treatment using at least 1% hypochlorite solution or any other equivalent chemical reagent. It must be ensured that chemical treatment ensures disinfection.
Mutilation/shredding must be such so as to prevent unauthorized reuse.
There will be no chemical pretreatment before incineration. Chlorinated plastics shall not be incinerated.
Deep burial shall be an option available only in towns with population less than five lakhs and in rural areas.
Colour coding and type of container for disposal of bio-medical wastes
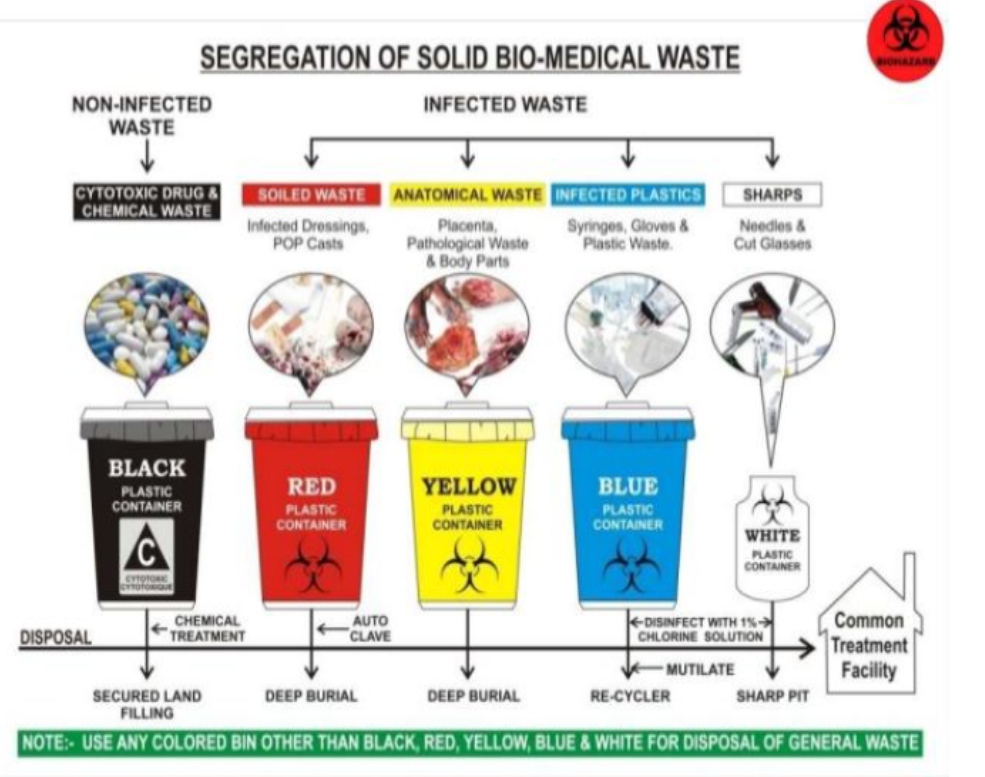






IMPORATANT: This is very important to keep in mind to make sure that you or your staff are disposing off the biomedical and biohazardous waste in a correct manner.
- General Waste: No risk to human health. Ex: Office paper, wrappers, general sweeping waste etc.
- Pathological Waste: Human Tissue or fluid Ex: Body Fluids, Body Tissue, body parts (extracted tooth, excised soft tissue).
- Sharps: Sharp Waste items which can lead to pricking or cutting type injury to others Ex: Needles, Scalpers, Knives, BP Blades.
- Infectious Waste: These are substances or items which can transmit bacterial, viral or parasitic disease to other humans who come in contact with it. These waste items are suspected to contain pathogens in it. Ex: Laboratory waste, used cotton or Gauze, tissue swabs, bandages, suture material.
- Chemical Waste: These are chemicals that are used in dental treatments or diagnosis. Ex: Laboratory reagent, disinfectants, X-ray film developers.
- Pharmaceutical waste: Expired or outdated drugs
- Pressurized containers: Gas Cylinders, aerosol cans.
- Genotoxic Waste: Waste containing Cytotoxic Drugs used in Cancer therapy
Emergency Procedure
It is the responsibility of the PI to make appropriate notifications in the wake of an occupational exposure, laboratory accident, loss of potential containment. PI should maintain a document accessible to all lab personnel, with a list of procedures to be followed in case of an accident such as a spill, injection, ingestion, aerosolization, splash, etc. The document should have the information on agent specific actions, known first aid procedures, effective disinfectants / neutralizing agents (include location in lab), and known symptoms associated with exposures to the agent(s). In case of emergency, please call Principal Investigator, Security, emergency medical personnel etc., and inform the IBSC.
The IBSC should be notified of incidents or adverse events involving biological agents or toxins.
In case of accidental exposure to infectious material e.g., infected body fluid, pathogenic strains etc., prophylaxis measures should be initiated as follows
- Immediate repeated washing with soap, water, antiseptic solution (where applicable)
- Report to respective PI and the Biosafety Officer
- Initiation of post-exposure counselling and testing and treatment (as applicable)